President Donald Trump’s bold tariff policies in 2025 are reshaping the US economy and global trade landscape. With proposed tariff rates as high as 70% on certain countries, these measures are creating significant uncertainty, raising inflation risks, and impacting consumer demand. This blog explores the details of Trump’s tariff plans, their effects on the US economy, and the responses from key trading partners like China, the European Union (EU), and Canada.
The Scope of Trump’s Tariff Plans
In April 2025, President Trump issued Executive Order 14257, leveraging the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA) to impose “reciprocal tariffs” on nearly all US trading partners. The average effective US tariff rate jumped from 2.5% to an estimated 27% between January and April 2025, the highest in over a century, before moderating to 15.8% by June 17 after partial rollbacks. Key measures include:
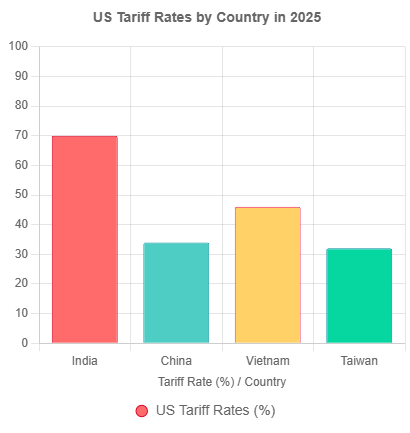
- Country-Specific Tariffs: Rates reaching 70% on countries like India, 34% on China, 46% on Vietnam, and 32% on Taiwan.
- Product-Specific Tariffs: Steel and aluminum tariffs doubled to 50% on March 12, 2025, with a 25% tariff introduced on imported cars.
- China Tariffs: Tariffs on Chinese goods peaked at 145% before dropping to 30% after trade negotiations, with de minimis shipments facing a 54% duty or a $100-$200 flat fee.
These tariffs aim to reduce the US trade deficit, which exceeded $1 trillion in 2023, and bolster American manufacturing and national security. However, they pose significant risks to the US economy, as outlined below.
Impacts on the US Economy
Economists warn that Trump’s tariffs could destabilize the US economy by driving inflation and softening consumer demand. The Penn Wharton Budget Model projects an 8% GDP reduction and a 7% wage drop, with middle-income households facing a $58,000 lifetime loss. The Tax Foundation estimates an average annual tax increase of $1,200 per US household in 2025 due to higher import costs. Key impacts include:
- Inflation Surge: Tariffs are projected to increase Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) prices by 1–1.5% in 2025, with peak effects expected this summer. For instance, a 46% tariff on Vietnamese shoes could raise costs for US retailers, directly impacting consumers.
- Weaker Consumer Demand: Higher prices for goods like electronics, clothing, and food may reduce purchasing power, particularly for lower-income households. The Yale Budget Lab forecasts a 0.6% GDP decline in 2025 and long-term losses of $80–110 billion annually.
- Business Uncertainty: The unpredictable tariff policy has disrupted supply chains and reduced business investment, with the Economic Policy Uncertainty Index doubling since January 2025.
Global Trade Responses
US-China Trade Dynamics
The US economy has been affected by eased export restrictions on China, particularly for chip design software and ethane, indicating a partial détente. After trade talks in Geneva, both nations agreed to a 90-day tariff reduction, lowering US tariffs on Chinese goods to 30% and Chinese tariffs on US goods to 10%. However, Trump has accused China of violating this truce, threatening renewed escalation.
EU Negotiations
The EU, facing a 20% tariff (reduced to 10% until July 8), is negotiating exemptions for pharmaceuticals, alcohol, semiconductors, and commercial aircraft. European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen is pushing for a “zero-for-zero” tariff agreement, pausing retaliatory measures to diversify trade.
Canada’s Strategic Move
Canada eliminated its digital services tax on US tech firms to resume trade talks, avoiding a 25% tariff on its goods. This decision followed Trump’s suspension of negotiations after Canada implemented the tax, underscoring the delicate balance in US-Canada trade relations.
Looking Ahead
As the July 9, 2025, tariff deadline nears, over 100 countries are engaging with the US to secure favorable trade terms. However, the Court of International Trade’s May 28 ruling declared some IEEPA-based tariffs illegal, though they remain in effect pending appeal. The US economy faces continued market volatility, with the S&P 500 recording its worst drop since June 2020 on April 3, 2025.
Conclusion
President Trump’s 2025 tariff plans, with rates up to 70%, are a high-stakes gamble for the US economy. While aimed at protecting American interests, they risk fueling inflation, weakening consumer demand, and straining global trade relations. As the US navigates negotiations with China, the EU, and Canada, the US economy remains at a crossroads. Stay informed as these developments unfold.




Pingback: US imposes heavy tariff on 14 countries